|
BACKGROUND
For centuries China stood as a leading civilization, outpacing the rest of the world in the arts, medicine and sciences. But in the 19th and early 20th centuries, China was beset by civil unrest, major famines, military defeats, and foreign occupation. After World War II, the Communists under MAO Zedong established a dictatorship that, while ensuring China’s sovereignty, imposed strict controls over everyday life and cost the lives of tens of millions of people. After 1978, his successor DENG Xiaoping gradually introduced market-oriented reforms and decentralized economic decision-making. Output quadrupled by 2000. Political controls remain tight while economic controls continue to be relaxed.
LOCATION
Eastern Asia, bordering the East China Sea, Korea Bay, Yellow Sea, and South China Sea, between North Korea and Vietnam.
Area: total 9,596,960 sg km
Currency Code: Yuan( CNY or RMB)
Exchange Rate: per dollar---6.90 CNY (2016)
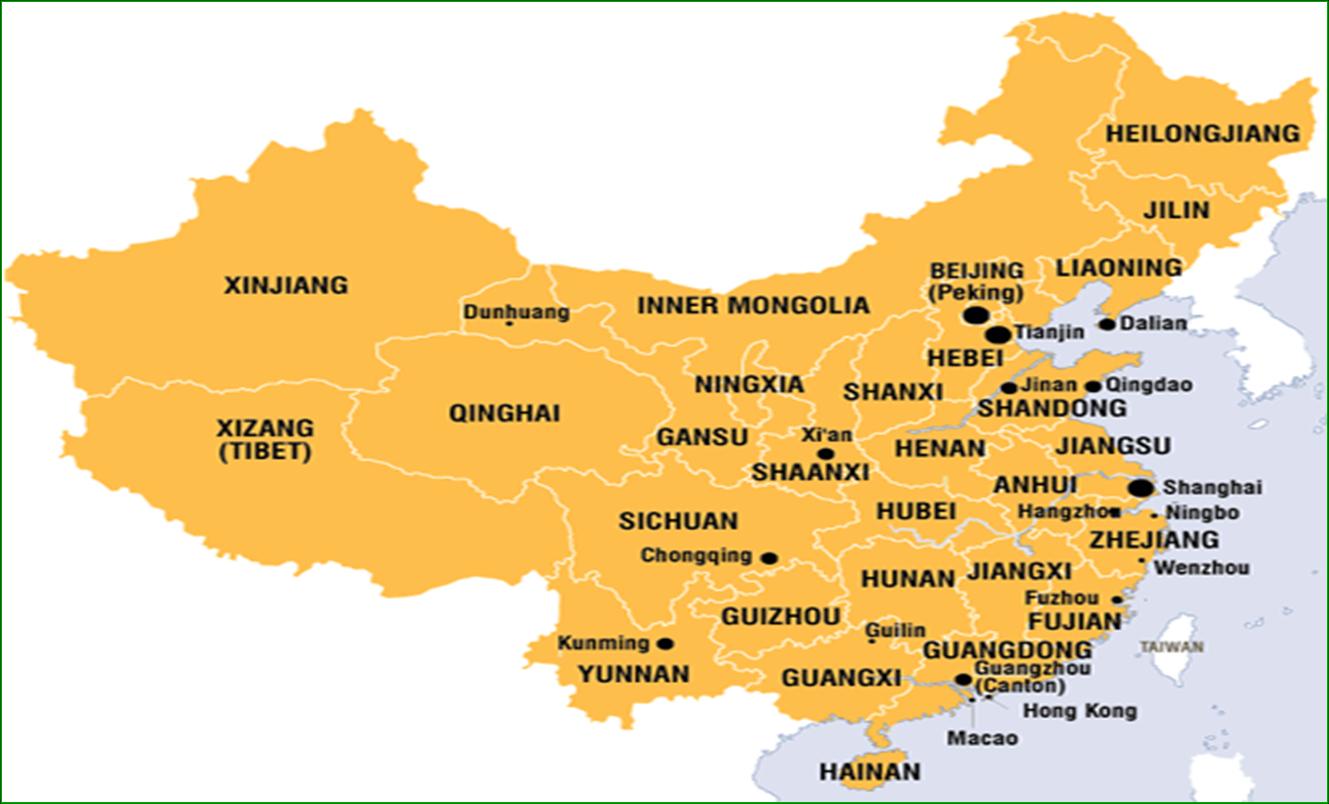
ADMINISTRATIVE DIVISIONS
China has 23 provinces, 5 autonomous regions, 4 municipalities and 2 Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macao).
ECONOMY-OVERVIEW
In late 1978 the Chinese leadership began moving the economy from a sluggish, inefficient, Soviet-style centrally planned economy to a more market-oriented system. Whereas the system operates within a political framework of strict Communist control, the economic influence of non-state organizations and individual citizens has been steadily increasing. The authorities switched to a system of household and village responsibility in agriculture in place of the old collectivization increased the authority of local officials and plant managers in industry, permitted a wide variety of small-scale enterprises in services and light manufacturing, and opened the economy to increased foreign trade and investment. The result has been a quadrupling of GDP since 1978. measured on a purchasing power parity basis, in 2004, China stood as the second-largest economy in the world after the US , although in per capita terms the country is still poor. Agriculture and industry have posted major gains, especially in coastal areas near Hong Kong and opposite Taiwan, where foreign investment has helped spur output of both domestic and export goods. The leadership, however, often has experienced - as a result of its hybrid system - the worst results of socialism (bureaucracy and lassitude) and of capitalism (windfall gains and growing income disparities). China thus has periodically backtracked, retightening central controls at intervals. The government has struggled to (a) collect revenues due from provinces, businesses, and individuals; (b) reduce corruption and other economic crimes; and (c) keep afloat the large state-owned enterprises, many of which had been shielded from competition by subsidies and had been losing the ability to pay full wages and pensions. From 100 to 150 million surplus rural workers are adrift between the villages and the cities, many subsisting through part-time low-paying jobs. Popular resistance, changes in central policy, and loss of authority by rural cadres have weakened China’s population control program, which is essential to maintaining long-term growth in living standards. Another long-term threat to growth is the deterioration in the environment, notably air pollution, soil erosion, and the steady fall of the water table especially in the north. China continues to lose arable land because of erosion and economic development. Beijing says it will intensify efforts to stimulate growth through spending on infrastructure - such as water control and power grids - and poverty relief and through rural tax reform aimed at eliminating arbitrary local levies on farmers. Accession to the World Trade Organization helps strengthen China’s ability to maintain strong growth rates but at the same time puts additional pressure on the hybrid system of strong political controls and growing market influences. China has benefited from a huge expansion in computer internet use, with 94 million users at the end of 2004. Foreign investment remains a strong element in china’s remarkable economic growth. Shortages of electric power and raw materials may affect industrial output in 2005. More power generating capacity is schedules to come online in 2006. In its rivalry with India as an economic power, China has a lead in the absorption of technology, the rising prominence in world trade, and the alleviation of poverty; India has one important advantage in its relative mastery of the English language, but the number of competent Chinese English-speakers is growing rapidly.
HISTORY
China, one of the four oldest civilizations in the world, has a written history of 4,000 years and boasts rich cultural relics and historical sites. It is the inventor of compass, paper, gunpowder and printing. The Great Wall, the Grand Canal and the Karez irrigation systems are three great ancient engineering projects built 2,000 years ago. Now they are the symbols of the rich culture heritage of the Chinese nation. China has gone over a long history of primitive society, slavery society, feudal society and semi-feudal semi-colonial society and the present socialist society.
CLIMATE
Extremely diverse; tropical in South to Sub arctic in North
LANGUAGES
The national language is Putonghua (the common speech) or Mandarin, which is one of the five working languages at the United Nations. Most of the 55 minority nationalities have their own languages. Cantonese is one of the local dialects of southern China. As a written language, Chinese has been used for 6,000 years.
|


 Study Abroad in China
Study Abroad in China Wenzhou Medical College
Wenzhou Medical College